Providing basic medical care to a person who has unexpectedly become ill or injured is known as first aid.
First aid can also refer to the initial help provided to someone having a medical emergency. With the help of this support, they might be able to survive until help arrives.
In other instances, first aid refers to the treatment of a small injury. For example, minor burns, wounds, and insect stings can frequently be treated with just first aid.
Things you should consider when providing first aid:
- Quickly and calmly assess the circumstances.
- Keep yourself and others safe from any harm.
- Make sure there is no contamination between you and them.
- First aid should be administered after assessing the casualty.
- Arrange support if needed.
- Reassuring and comforting.
Purpose & Principles of First Aid
The purpose of first aid is to give an injured or ill individual emergency care while waiting for professional medical assistance. Its objectives are to maintain life, stop additional harm or disease, and encourage recovery. When administering this basic care, the first aid principles serve as a guide. Here is a brief explanation of first aid’s goals and guiding principles.

Purpose of First Aid:
Preserve Life
Saving lives is the main goal of first aid. It entails evaluating the patient’s health, making sure their airway is unobstructed, and offering measures to support breathing and circulation.
Prevent Further Harm
The goal of first aid is to stop the injury or sickness from getting worse. Prompt interventions can lessen future harm by stopping bleeding, immobilising fractures, or removing the victim from hazardous conditions.
Promote Recovery
First aid interventions can aid the patient’s recovery. First aid can help relieve pain, lessen complications, and increase the likelihood of a full recovery by giving proper attention and support.
Principles of First Aid:
Preserve Safety
The first concern is the safety of the injured party, the first responder, and everyone else present. Make sure the place is risk-free before offering any assistance, and take the necessary measures to reduce dangers.
Assess the Situation
Analyse the condition to assess its severity and type. Determine the best course of action by evaluating the person’s vital signs, state of consciousness, and any imminent dangers.
Prioritize Care
Life-threatening situations including heart arrest, severe bleeding, or closed airways should be attended to very away. Before tackling the less urgent issues, take care of these important ones first.
Seek Professional Help
It is crucial to call emergency medical services (EMS) or seek expert medical help as soon as you can in dangerous or complex instances. First aid cannot replace seeking expert medical attention.
Provide Comfort and Reassurance
In dangerous or complicated situations, it’s critical to contact emergency medical services (EMS) or seek professional medical assistance as soon as you can. First aid cannot take the place of obtaining specialised medical care.
Use Available Resources
Make use of the resources and equipment at your disposal to perform first aid efficiently. This covers first aid supplies, safety gear, and any support from onlookers or skilled professionals.
Role & Responsibilities of First Aider
The patient’s life should always be your top priority when doing first aid, regardless of whether you treat a wound or perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Because of this, the first aider should be qualified & certified in first aid courses & knowing the three components of first aid training is necessary as well.
If you familiarise yourself with the goals of first aid, you will be able to identify what actions to do as a first responder in the event of an emergency.
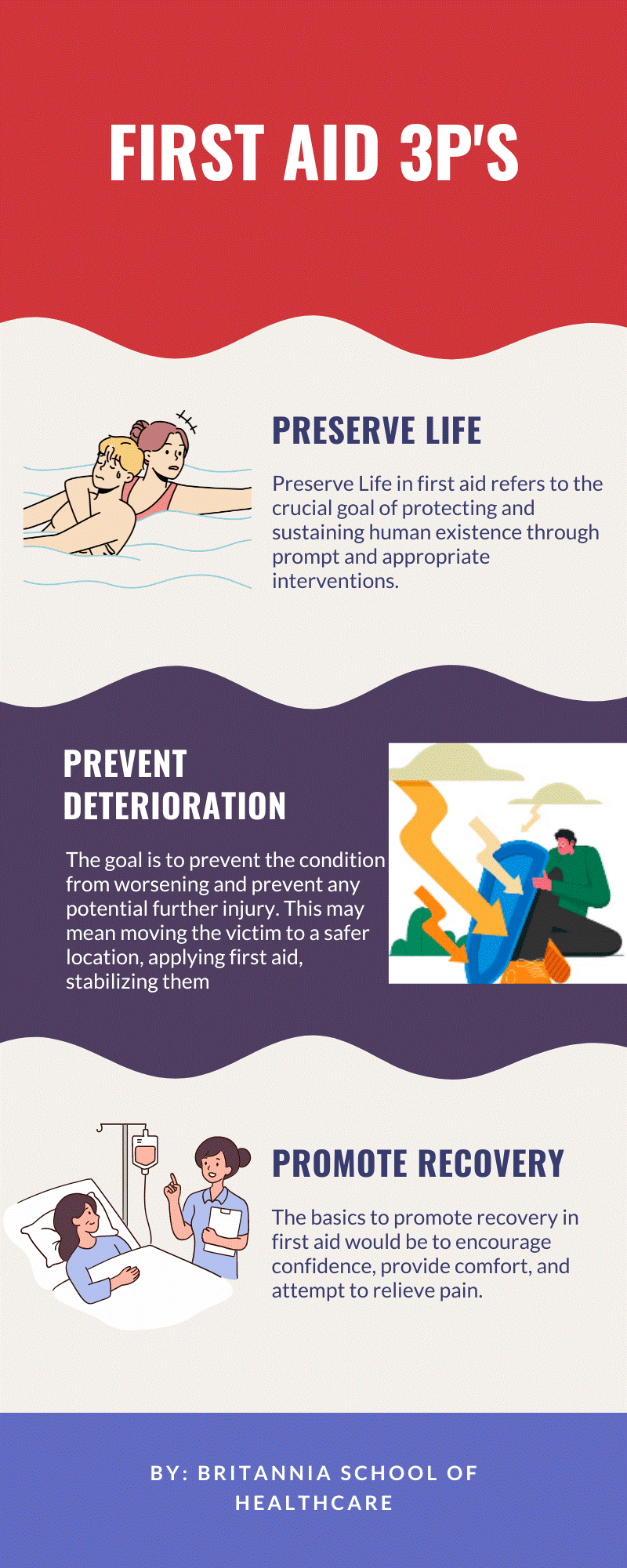
The Aims of the First Aid-Three P’s
1. Preserve Life
The primary goal of a first-aider is to save lives. The first aider’s top goal while dealing with an injured or ill person is to assess the situation and take the required steps to save lives. This could entail conducting life-saving procedures including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), unblocking airways, or utilising an automated external defibrillator (AED) in cardiac arrest situations. The primary concern of the first aider is to maintain or re-establish the victim’s essential processes, such as breathing and circulation. First responders play a crucial role in preserving life and giving the injured or ill individual the best chance of survival until professional medical care arrives by reacting quickly and effectively to life-threatening situations.
2. Prevent Deterioration
One of the most important aspects of a first aider’s job is preventing degradation. The first responder must continue to keep an eye on the patient’s condition after the initial care has been given to spot any signs of worsening. This entails keeping an eye on the body’s vital signs, checking for any changes in breathing or consciousness, and keeping an eye out for any new or escalating symptoms. The first responder can take the necessary steps to stop further damage or problems by quickly identifying indicators of deterioration. This can entail shifting the patient’s position, providing extra first aid treatments, or contacting an advanced medical professional. The first responder’s attention to detail and proactive attitude is crucial in maintaining the patient’s condition and reducing the possibility of further deterioration.
3. Promote Recovery
One of a first aider’s most important responsibilities is encouraging recovery. After giving the victim emergency care and stabilising their condition, the first responder works to aid in their recovery. This entails establishing a welcoming and secure setting, providing assurance and emotional support, and ensuring proper follow-up care. First responders contribute to the person’s physical and mental well-being by encouraging recovery. They can offer advice on self-care techniques, urge the patient to seek extra medical help if necessary, and provide resources or information for further support. The first responder’s responsibility for supporting recovery goes beyond the initial response; it also emphasises the value of compassionate care for the patient’s long-term rehabilitation.
DR ABC: The Fundamental Steps of First Aid Assessment and Response
A frequent first aid abbreviation is DR ABC, which makes it easy to recall the importance of an injury or illness when examining and treating the patient. Each letter denotes a particular duty to be performed:
D-Danger: Consider any potential risks to yourself, the person in need, and others before proceeding. Before approaching or offering assistance, make sure it is safe.
R-Responce:
Make sure the person is conscious. Check to see if they are responding or not. Gently tap their shoulders and inquire as to their well-being.
A-Airway: Tilt the person’s head back and elevate their chin to widen their airway. This facilitates the free movement of air into and out of the lungs.
B-Breathing: Look, listen, and feel for indications that you are breathing. Check your chest for motions, listen for breathing noises, and feel your cheek for airflow. Start rescue breathing if the person is not breathing, or CPR if necessary.
C-Circulation:Look for a pulse or other indications of circulation. Check for a pulse and other indications of circulation, such as regular breathing or movement. Start CPR as soon as possible if there is no pulse.
First responders can prioritise their tasks and deliver crucial care methodically and effectively by using the DR ABC technique. In the early phases of administering first aid, it emphasises the crucial significance of ensuring safety, evaluating the response, preserving a clear airway, checking to breathe, and attending to circulation.
FAQs
The validity of an occupational first aid certification is two years, after which recertification training is necessary.
Giving tablets or medication is not addressed in first aid at work training, except utilising aspirin to treat a casualty with a suspected heart attack, which is covered in our one-day first aid at work course.
First aid is the treatment provided to an ill or injured person before trained medical assistance is available.
An emergency can be saved by qualified first aiders, who are not only required by law in the workplace. Additionally, it demonstrates that a business owner must be concerned about the company’s and its workers’ security.
All of these topics are covered in one of our Level 3 Award in Paediatric First Aid and Level 3 Award in Emergency Paediatric First Aid courses.


