People frequently consult with professionals such as nutritionists or dietitians when it comes to medical nutrition therapy, weight management, or healthy eating. Many people assume that a dietitian and a nutritionist are the same. However, these terms are frequently used interchangeably, creating confusion for those seeking expert guidance.
Despite their shared focus on food and health, dietitians and nutritionists differ significantly in qualifications, legal status, and professional scope. This blog delineates the essential differences to assist you in making an informed decision, whether you seek nutritional guidance or are investigating relevant information.
Key Takeaways
- RD (Registered Dietitian): Traditional title used for many years.
- RDN (Registered Dietitian Nutritionist): A newer, optional title adopted in the United States by the Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR) in 2013. It includes the word “nutritionist” to reflect the broader scope of practi
- A dietitian is a regulated healthcare professional qualified to provide medical nutrition therapy, while a nutritionist offers general dietary advice and is not always legally regulated.
What is Dietitian?
dietitian is a highly qualified health professional who specialises in the science of nutrition and dietetics. Dietitians are trained to assess, diagnose, and treat dietary and nutritional problems at both individual and population levels. Their expertise is grounded in evidence-based practice, and they often work closely with doctors and other healthcare providers.
In many countries, qualified dietitians hold the professional titles of Registered Dietitian (RD) or Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN), both of which signify that the individual has met rigorous educational, clinical, and regulatory standards required for professional registration and practice.
What is Nutritionist?
A nutritionist is someone who advises people on how to improve their overall diet and lifestyle. However, the term “nutritionist” is not consistently regulated across countries, which means that the level of training and credibility can vary significantly.
Global Differences in Terminology
United Kingdom: Only dietitians are legally regulated by HCPC. The term nutritionist can be used more loosely unless registered with AfN.
United States: Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) is the official credential. The term nutritionist may or may not indicate formal training.
Canada and Australia: Similar regulations apply, dietitian is a protected title, while nutritionist is not always regulated.
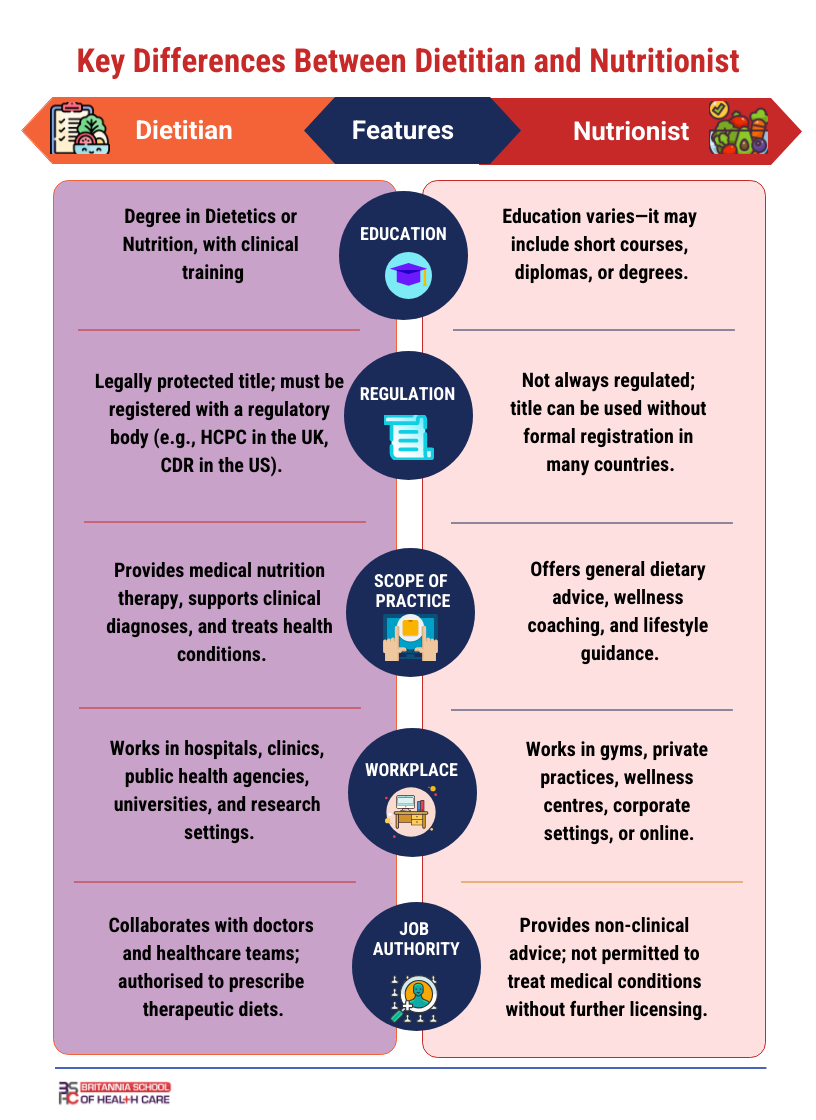
What is the Difference between a Nutritionist and a Dietitian?
While both nutritionists and dietitians are professionals who focus on food and its impact on health, there are key differences in their qualifications, scope of practice, and legal recognition. Understanding these distinctions is essential for individuals seeking expert dietary advice or pursuing a career in the field of nutrition.
1. Regulation and Legal Protection
The title “dietitian” is legally protected and regulated in many countries, including the UK, US, Canada, and Australia. In contrast, the title “nutritionist” is not consistently regulated. In many regions, anyone can call themselves a nutritionist, regardless of formal training.
In the UK, for instance, dietitians must be registered with the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC), and in the US, dietitians hold titles such as Registered Dietitian (RD) or Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN). These credentials require accredited education, supervised practice, and successful completion of a national registration exam. However, some countries or organisations offer voluntary registration for qualified nutritionists, such as the Association for Nutrition (AfN) in the UK, which grants the title of Registered Nutritionist (RN) to those who meet certain professional standards.
2. Education and Training
Dietitians are required to complete a recognised degree in dietetics or nutrition. Nutritionists, on the other hand, may have varying levels of education, ranging from short courses or diplomas to full university degrees.
3. Scope of Practice
Dietitians are qualified to work in clinical settings and provide medical nutrition therapy. Nutritionists typically provide general guidance on healthy eating, weight management, and lifestyle.
4. Professional Accountability
Dietitians are held accountable by statutory regulatory bodies and must adhere to strict codes of professional conduct. Nutritionists, unless registered with a professional body, may not be subject to the same regulatory oversight, which can lead to variability in the quality and credibility of services provided.
Final Thoughts
In summary, while both dietitians and nutritionists play valuable roles in promoting health and nutrition, dietitians are legally regulated healthcare professionals with the authority to provide medical nutrition therapy, whereas nutritionists typically focus on general health and wellness and may not require formal registration or clinical training. When seeking professional dietary support, it is important to consider the nature of your health needs and verify the practitioner’s qualifications to ensure safe, effective, and evidence-based guidance.

